|
|
RT-Thread 内核介绍
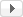
内核是操作系统最基础也是最重要的部分。下图为 RT-Thread 内核架构图,内核处于硬件层之上,内核部分包括内核库、实时内核实现。
RT-Thread 内核及底层结构
内核库是为了保证内核能够独立运行的一套小型的类似 C 库的函数实现子集。这部分根据编译器的不同自带 C 库的情况也会有些不同,当使用 GNU GCC 编译器时,会携带更多的标准 C 库实现。
线程调度
线程是 RT-Thread 操作系统中最小的调度单位,线程调度算法是基于优先级的全抢占式多线程调度算法,即在系统中除了中断处理函数、调度器上锁部分的代码和禁止中断的代码是不可抢占的之外,系统的其他部分都是可以抢占的,包括线程调度器自身。
线程控制块
在 RT-Thread 中,线程控制块由结构体 struct rt_thread 表示,线程控制块是操作系统用于管理线程的一个数据结构,它会存放线程的一些信息,例如优先级、线程名称、线程状态等,也包含线程与线程之间连接用的链表结构,线程等待事件集合等,详细定义如下:
- /* 线程控制块 */
- struct rt_thread
- {
- /* rt 对象 */
- char name[RT_NAME_MAX]; /* 线程名称 */
- rt_uint8_t type; /* 对象类型 */
- rt_uint8_t flags; /* 标志位 */
- rt_list_t list; /* 对象列表 */
- rt_list_t tlist; /* 线程列表 */
- /* 栈指针与入口指针 */
- void *sp; /* 栈指针 */
- void *entry; /* 入口函数指针 */
- void *parameter; /* 参数 */
- void *stack_addr; /* 栈地址指针 */
- rt_uint32_t stack_size; /* 栈大小 */
- /* 错误代码 */
- rt_err_t error; /* 线程错误代码 */
- rt_uint8_t stat; /* 线程状态 */
- /* 优先级 */
- rt_uint8_t current_priority; /* 当前优先级 */
- rt_uint8_t init_priority; /* 初始优先级 */
- rt_uint32_t number_mask;
- ......
- rt_ubase_t init_tick; /* 线程初始化计数值 */
- rt_ubase_t remaining_tick; /* 线程剩余计数值 */
- struct rt_timer thread_timer; /* 内置线程定时器 */
- void (*cleanup)(struct rt_thread *tid); /* 线程退出清除函数 */
- rt_uint32_t user_data; /* 用户数据 */
- };
其中 init_priority 是线程创建时指定的线程优先级,在线程运行过程当中是不会被改变的(除非用户执行线程控制函数进行手动调整线程优先级)。cleanup 会在线程退出时,被空闲线程回调一次以执行用户设置的清理现场等工作。最后的一个成员 user_data 可由用户挂接一些数据信息到线程控制块中,以提供类似线程私有数据的实现。
时间片轮转和抢占
当我们创建一个或者多个任务之后,系统具体是怎么进行时间片计算和任务抢占的呢?主要涉及到两个中断函数:SysTick_Handler()和PendSV_Handler(),以及任务计划函数rt_schedule()*核心**
任务计划函数rt_schedule()具体实现
- // schedule.c
- /**
- * This function will perform one schedule. It will select one thread
- * with the highest priority level, then switch to it.
- */
- void rt_schedule(void)
- {
- rt_base_t level;
- struct rt_thread *to_thread;
- struct rt_thread *from_thread;
- /* disable interrupt */
- level = rt_hw_interrupt_disable();
- /* check the scheduler is enabled or not */
- if (rt_scheduler_lock_nest == 0)
- {
- rt_ubase_t highest_ready_priority;
- if (rt_thread_ready_priority_group != 0)
- {
- /* need_insert_from_thread: need to insert from_thread to ready queue */
- int need_insert_from_thread = 0;
- to_thread = _get_highest_priority_thread(&highest_ready_priority);
- if ((rt_current_thread->stat & RT_THREAD_STAT_MASK) == RT_THREAD_RUNNING)
- {
- if (rt_current_thread->current_priority < highest_ready_priority)
- {
- to_thread = rt_current_thread;
- }
- else
- {
- need_insert_from_thread = 1;
- }
- }
- /* higher priority thread is not equal to the current one, switch to run the higher one */
- if (to_thread != rt_current_thread)
- {
- /* if the destination thread is not the same as current thread */
- rt_current_priority = (rt_uint8_t)highest_ready_priority;
- from_thread = rt_current_thread;
- rt_current_thread = to_thread;
- RT_OBJECT_HOOK_CALL(rt_scheduler_hook, (from_thread, to_thread));
- if (need_insert_from_thread)
- {
- rt_schedule_insert_thread(from_thread);
- }
- rt_schedule_remove_thread(to_thread);
- to_thread->stat = RT_THREAD_RUNNING | (to_thread->stat & ~RT_THREAD_STAT_MASK);
- /* switch to new thread */
- RT_DEBUG_LOG(RT_DEBUG_SCHEDULER,
- ("[%d]switch to priority#%d "
- "thread:%.*s(sp:0x%08x), "
- "from thread:%.*s(sp: 0x%08x)n",
- rt_interrupt_nest, highest_ready_priority,
- RT_NAME_MAX, to_thread->name, to_thread->sp,
- RT_NAME_MAX, from_thread->name, from_thread->sp));
- #ifdef RT_USING_OVERFLOW_CHECK
- _rt_scheduler_stack_check(to_thread);
- #endif
- if (rt_interrupt_nest == 0)
- {
- extern void rt_thread_handle_sig(rt_bool_t clean_state);
- rt_hw_context_switch((rt_ubase_t)&from_thread->sp,
- (rt_ubase_t)&to_thread->sp);
- #ifdef RT_USING_SIGNALS
- if (rt_current_thread->stat & RT_THREAD_STAT_SIGNAL_PENDING)
- {
- extern void rt_thread_handle_sig(rt_bool_t clean_state);
- rt_current_thread->stat &= ~RT_THREAD_STAT_SIGNAL_PENDING;
- rt_hw_interrupt_enable(level);
- /* check signal status */
- rt_thread_handle_sig(RT_TRUE);
- }
- else
- {
- rt_hw_interrupt_enable(level);
- }
- #else
- /* enable interrupt */
- rt_hw_interrupt_enable(level);
- #endif
- goto __exit;
- }
- else
- {
- RT_DEBUG_LOG(RT_DEBUG_SCHEDULER, ("switch in interruptn"));
- rt_hw_context_switch_interrupt((rt_ubase_t)&from_thread->sp,
- (rt_ubase_t)&to_thread->sp);
- }
- }
- else
- {
- rt_schedule_remove_thread(rt_current_thread);
- rt_current_thread->stat = RT_THREAD_RUNNING | (rt_current_thread->stat & ~RT_THREAD_STAT_MASK);
- }
- }
- }
- /* enable interrupt */
- rt_hw_interrupt_enable(level);
- __exit:
- return;
- }
从以上源码可以看到,任务的优先级计算、状态切换等算法都是在这边完成的
而SysTick_Handler()和PendSV_Handler(),前者负责任务的运行状态检测,当发生抢占或者时间片轮转时,触发后者进行任务的上下文转换。
- // board.c
- /**
- * This is the timer interrupt service routine.
- *
- */
- void SysTick_Handler(void)
- {
- /* enter interrupt */
- rt_interrupt_enter();
- HAL_IncTick();
- rt_tick_increase();
- /* leave interrupt */
- rt_interrupt_leave();
- }
- // clock.c
- void rt_tick_increase(void)
- {
- struct rt_thread *thread;
- /* increase the global tick */
- #ifdef RT_USING_SMP
- rt_cpu_self()->tick ++;
- #else
- ++ rt_tick;
- #endif
- /* check time slice */
- thread = rt_thread_self();
- -- thread->remaining_tick;
- if (thread->remaining_tick == 0)
- {
- /* change to initialized tick */
- thread->remaining_tick = thread->init_tick;
- thread->stat |= RT_THREAD_STAT_YIELD;
- /* yield */
- rt_thread_yield();
- }
- /* check timer */
- rt_timer_check();
- }
通过查看源码可以看到,/ check time slice /部分是统计当前任务运行剩余的时间片,(thread->remaining_tick值),一旦当前任务时间片用完就调用rt_schedule()(在rt_thread_yield()会调用)进行任务状态切换,达到时间片轮转的功能。
以上看出来,系统心跳内部只检测了当前任务的时间片,并没有对其他任务进行检测,那抢占是如何触发的呢?
回到struct rthread的结构体我们可以看到,每一个任务都内嵌有一个定时器模块(struct rt_timer thread_timer; ),当任务调用rt_thread_mdelay()释放CPU资源时,定时器模块负责统计任务的挂起时间,每次插入定时器链表的时候,系统都会依据定时的超时时间进行有序排列(跳表 (Skip List) 算法),通过rt_timer_check()进行超时判断,就调用rt_schedule()进行任务状态切换,达到高优先级抢占的目的。
在PendSV_Handler()中断内任务才会进行真正的上下文切换,不同编译环境下的汇编源码有差别,但核心都是通过将任务运行的堆栈空间填充到CPU寄存器(R1-R11)
- ; r0 --> switch from thread stack
- ; r1 --> switch to thread stack
- ; psr, pc, lr, r12, r3, r2, r1, r0 are pushed into [from] stack
- PendSV_Handler PROC
- EXPORT PendSV_Handler
- ; disable interrupt to protect context switch
- MRS r2, PRIMASK
- CPSID I
- ; get rt_thread_switch_interrupt_flag
- LDR r0, =rt_thread_switch_interrupt_flag
- LDR r1, [r0]
- CBZ r1, pendsv_exit ; pendsv already handled
- ; clear rt_thread_switch_interrupt_flag to 0
- MOV r1, #0x00
- STR r1, [r0]
- LDR r0, =rt_interrupt_from_thread
- LDR r1, [r0]
- CBZ r1, switch_to_thread ; skip register save at the first time
- MRS r1, psp ; get from thread stack pointer
- STMFD r1!, {r4 - r11} ; push r4 - r11 register
- LDR r0, [r0]
- STR r1, [r0] ; update from thread stack pointer
- switch_to_thread
- LDR r1, =rt_interrupt_to_thread
- LDR r1, [r1]
- LDR r1, [r1] ; load thread stack pointer
- LDMFD r1!, {r4 - r11} ; pop r4 - r11 register
- MSR psp, r1 ; update stack pointer
- pendsv_exit
- ; restore interrupt
- MSR PRIMASK, r2
- ORR lr, lr, #0x04
- BX lr
- ENDP
总结
RT-Thread任务调度的时候,不是在系统的心跳中断内对每个任务进行优先级,时间片判断,而是单检测当前运行任务的时间片,并配合定时器模块,进行抢占。提高了运行效率。
|
|
![]() RT-Thread
4131 人阅读
|
0 人回复
|
2021-04-25
RT-Thread
4131 人阅读
|
0 人回复
|
2021-04-25
 /3
/3